KVBM Guide
Enable KV offloading using KV Block Manager (KVBM) for Dynamo deployments
The Dynamo KV Block Manager (KVBM) is a scalable runtime component designed to handle memory allocation, management, and remote sharing of Key-Value (KV) blocks for inference tasks across heterogeneous and distributed environments. It acts as a unified memory layer for frameworks like vLLM and TensorRT-LLM.
KVBM is modular and can be used standalone via pip install kvbm or as the memory management component in the full Dynamo stack. This guide covers installation, configuration, and deployment of the Dynamo KV Block Manager (KVBM) and other KV cache management systems.
Table of Contents
- Quick Start
- Run KVBM Standalone
- Run KVBM in Dynamo with vLLM
- Run KVBM in Dynamo with TensorRT-LLM
- Run Dynamo with SGLang HiCache
- Disaggregated Serving with KVBM
- Configuration
- Enable and View KVBM Metrics
- Benchmarking KVBM
- Troubleshooting
- Developing Locally
Quick Start
Run KVBM Standalone
KVBM can be used independently without using the rest of the Dynamo stack:
See the support matrix for version compatibility.
Build from Source
To build KVBM from source, see the detailed instructions in the KVBM bindings README.
Run KVBM in Dynamo with vLLM
Docker Setup
Aggregated Serving
Verify Deployment
Alternative: Using Direct vllm serve
You can also use vllm serve directly with KVBM:
Run KVBM in Dynamo with TensorRT-LLM
[!NOTE] Prerequisites:
- Ensure
etcdandnatsare running before starting- KVBM only supports TensorRT-LLM’s PyTorch backend
- Disable partial reuse (
enable_partial_reuse: false) to increase offloading cache hits- KVBM requires TensorRT-LLM v1.2.0rc2 or newer
Docker Setup
Aggregated Serving
Verify Deployment
Alternative: Using trtllm-serve
Run Dynamo with SGLang HiCache
SGLang’s Hierarchical Cache (HiCache) extends KV cache storage beyond GPU memory to include host CPU memory. When using NIXL as the storage backend, HiCache integrates with Dynamo’s memory infrastructure.
Quick Start
Learn more: See the SGLang HiCache Integration Guide for detailed configuration, deployment examples, and troubleshooting.
Disaggregated Serving with KVBM
KVBM supports disaggregated serving where prefill and decode operations run on separate workers. KVBM is enabled on the prefill worker to offload KV cache.
Disaggregated Serving with vLLM
Disaggregated Serving with TRT-LLM
[!NOTE] The latest TensorRT-LLM release (1.3.0rc1) is currently experiencing a request hang when running disaggregated serving with KVBM. Please include the TensorRT-LLM commit id
18e611da773026a55d187870ebcfa95ff00c8482when building the Dynamo TensorRT-LLM runtime image to test the KVBM + disaggregated serving feature.
[!NOTE] Important: After logging into the Dynamo TensorRT-LLM runtime container, copy the Triton kernels into the container’s virtual environment as a separate Python module.
Configuration
Cache Tier Configuration
Configure KVBM cache tiers using environment variables:
You can also specify exact block counts instead of GB:
DYN_KVBM_CPU_CACHE_OVERRIDE_NUM_BLOCKSDYN_KVBM_DISK_CACHE_OVERRIDE_NUM_BLOCKS
SSD Lifespan Protection
When disk offloading is enabled, disk offload filtering is enabled by default to extend SSD lifespan. The current policy only offloads KV blocks from CPU to disk if the blocks have frequency ≥ 2. Frequency doubles on cache hit (initialized at 1) and decrements by 1 on each time decay step.
To disable disk offload filtering:
Enable and View KVBM Metrics
Setup Monitoring Stack
Enable Metrics for vLLM
Enable Metrics for TensorRT-LLM
Firewall Configuration (Optional)
View Metrics
Access Grafana at http://localhost:3000 (default login: dynamo/dynamo) and look for the KVBM Dashboard.
Available Metrics
Benchmarking KVBM
Use LMBenchmark to evaluate KVBM performance.
Setup
Run Benchmark
Average TTFT and other performance numbers will be in the output.
TIP: If metrics are enabled, observe KV offloading and onboarding in the Grafana dashboard.
Baseline Comparison
vLLM Baseline (without KVBM)
TensorRT-LLM Baseline (without KVBM)
Troubleshooting
No TTFT Performance Gain
Symptom: Enabling KVBM does not show TTFT improvement or causes performance degradation.
Cause: Not enough prefix cache hits on KVBM to reuse offloaded KV blocks.
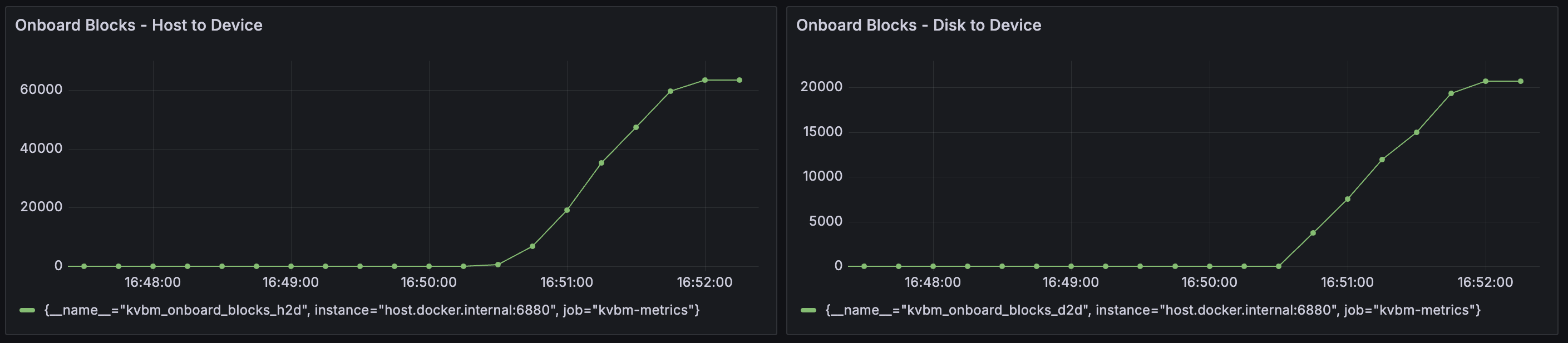
Solution: Enable KVBM metrics and check the Grafana dashboard for Onboard Blocks - Host to Device and Onboard Blocks - Disk to Device. Large numbers of onboarded KV blocks indicate good cache reuse:
KVBM Worker Initialization Timeout
Symptom: KVBM fails to start when allocating large memory or disk storage.
Solution: Increase the leader-worker initialization timeout (default: 1800 seconds):
Disk Offload Fails to Start
Symptom: KVBM fails to start when disk offloading is enabled.
Cause: fallocate() is not supported on the filesystem (e.g., Lustre, certain network filesystems).
Solution: Enable disk zerofill fallback:
If you encounter “write all error” or EINVAL (errno 22), also try:
Developing Locally
Inside the Dynamo container, after changing KVBM-related code (Rust and/or Python):
See Also
- KVBM Overview for a quick overview of KV Caching, KVBM and its architecture
- KVBM Design for a deep dive into KVBM architecture
- LMCache Integration
- FlexKV Integration
- SGLang HiCache