Distributed Tracing with Tempo
Overview
Dynamo supports OpenTelemetry-based distributed tracing for visualizing request flows across Frontend and Worker components. Traces are exported to Tempo via OTLP (OpenTelemetry Protocol) and visualized in Grafana.
Requirements: Set DYN_LOGGING_JSONL=true and OTEL_EXPORT_ENABLED=true to export traces to Tempo.
This guide covers single GPU demo setup using Docker Compose. For Kubernetes deployments, see Kubernetes Deployment.
Note: This section has overlap with Logging of OpenTelemetry Tracing since OpenTelemetry has aspects of both logging and tracing. The tracing approach documented here is for persistent trace visualization and analysis. For short debugging sessions examining trace context directly in logs, see the Logging guide.
Environment Variables
Getting Started Quickly
1. Start Observability Stack
Start the observability stack (Prometheus, Grafana, Tempo, exporters). See Observability Getting Started for instructions.
2. Set Environment Variables
Configure Dynamo components to export traces:
3. Start Dynamo Components (Single GPU)
For a simple single-GPU deployment, start the frontend and a single vLLM worker:
This runs both prefill and decode on the same GPU, providing a simpler setup for testing tracing.
Alternative: Disaggregated Deployment (2 GPUs)
Run the vLLM disaggregated script with tracing enabled:
Note: the example vLLM disagg.sh sets additional per-worker port environment variables (e.g., DYN_VLLM_KV_EVENT_PORT,
VLLM_NIXL_SIDE_CHANNEL_PORT) to avoid ZMQ “Address already in use” conflicts when multiple workers run on the same host. If you run the components manually, make sure you mirror those port settings.
For disaggregated deployments, this separates prefill and decode onto different GPUs for better resource utilization.
4. Generate Traces
Send requests to the frontend to generate traces (works for both aggregated and disaggregated deployments). Note the x-request-id header, which allows you to easily search for and correlate this specific trace in Grafana:
5. View Traces in Grafana Tempo
- Open Grafana at
http://localhost:3000 - Login with username
dynamoand passworddynamo - Navigate to Explore (compass icon in the left sidebar)
- Select Tempo as the data source (should be selected by default)
- In the query type, select “Search” (not TraceQL, not Service Graph)
- Use the Search tab to find traces:
- Search by Service Name (e.g.,
dynamo-frontend) - Search by Span Name (e.g.,
http-request,handle_payload) - Search by Tags (e.g.,
x_request_id=test-trace-001)
- Search by Service Name (e.g.,
- Click on a trace to view the detailed flame graph
Example Trace View
Below is an example of what a trace looks like in Grafana Tempo:
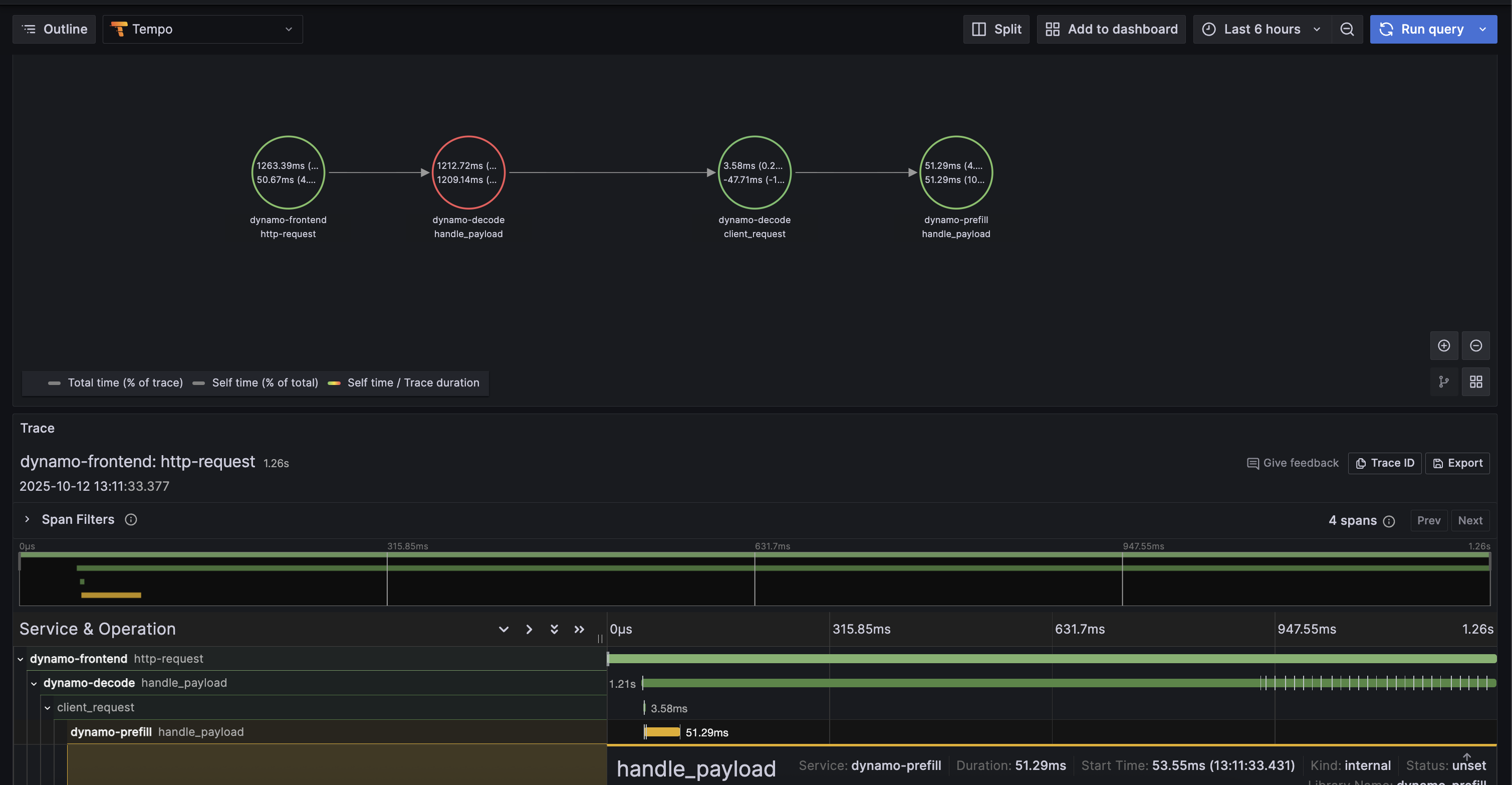
6. Stop Services
When done, stop the observability stack. See Observability Getting Started for Docker Compose commands.
Kubernetes Deployment
For Kubernetes deployments, ensure you have a Tempo instance deployed and accessible (e.g., http://tempo.observability.svc.cluster.local:4317).
Modify DynamoGraphDeployment for Tracing
Add common tracing environment variables at the top level and service-specific names in each component in your DynamoGraphDeployment (e.g., examples/backends/vllm/deploy/disagg.yaml):
Apply the updated DynamoGraphDeployment:
Traces will now be exported to Tempo and can be viewed in Grafana.